What is a LAN cable used for?
A LAN cable, or Ethernet cable, is used to connect devices within a local area network (LAN) for data transmission, enabling communication between computers, servers, switches, and routers. It provides internet access by connecting devices to a modem or router and offers a stable, reliable connection with lower latency and higher speeds compared to wireless options. Additionally, LAN cables enhance security, as they require physical access for data interception, making them essential for wired networks in homes, offices, and data centers.

Ethernet Cable Categories
Ethernet cables are categorized based on their performance characteristics and specifications. Here are some common categories
| Category | Maximum Speed | Maximum Frequency | Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cat 5 | 100 Mbps | 100 MHz | Mostly outdated |
| Cat 5E | 1 Gbps | 100 MHz | Enhanced to reduce crosstalk |
| Cat 6 | 10 Gbps* | 250 MHz | Better performance, reduced interference |
| Cat 6A | 10 Gbps | 500 MHz | Augmented for longer distances |
| Cat 7 | 10 Gbps | 600 MHz | Shielded to reduce interference |
| Cat 8 | 25/40 Gbps | 2000 MHz | Designed for data centers, enhanced shielding |
*Note: Cat 6 supports 10 Gbps for shorter distances (up to 55 meters).
How many conductors does a LAN cable have?
A standard LAN cable, such as Cat 5E, Cat 6, or higher, typically has 8 conductors. These conductors are twisted into 4 pairs to reduce crosstalk and electromagnetic interference.
UTP vs FTP vs STP,which is better?
The choice between STP, UTP, and FTP cables depends on your specific needs and environment:
1. UTP (Unshielded Twisted Pair): Consists of twisted pairs of wires without any additional shielding.
- Pros: Most competative, more flexible, easier to install.
- Cons: Less protection against electromagnetic interference (EMI).
- Best for: suitable for most home and small office environments, with minimal interference.
2. STP (Shielded Twisted Pair): Each pair of wires is shielded with an additional layer of protection.
- Pros: Better protection against EMI due to individual shielding of each pair.
- Cons: More expensive, less flexible, requires grounding.
- Best for: Ideal for high-interference areas.
3. FTP (Foiled Twisted Pair): All pairs are wrapped together in a single foil shield.
- Pros: A foil shield around all pairs provides good EMI protection.
- Cons: More expensive than UTP, requires grounding.
- Best for: Environments with moderate EMI, such as office buildings.
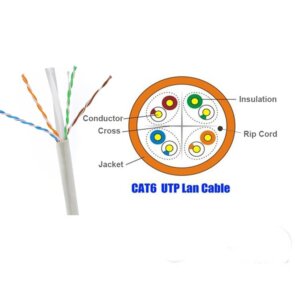
Cat.6 UTP Cable
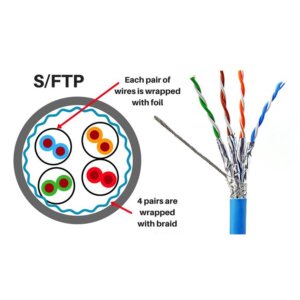
Cat.6A SFTP Cable
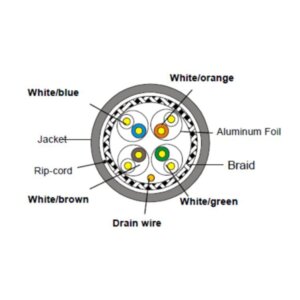
Cat.7 SFTP Cable
What are the conductors in the Ethernet cable?
In LAN cables, the main types of conductors used are:
Solid Copper, Stranded Copper, Copper-Clad Aluminum (CCA) and Pure Aluminum
1. Solid Copper
- Description: A single, solid copper wire per conductor.
- Use: Ideal for permanent installations and longer runs.
- Pros: Lower attenuation, better performance over long distances.
- Cons: Less flexible, can break with repeated bending.
2. Stranded Copper
- Description: Multiple thin copper strands twisted together per conductor.
- Use: Suitable for patch cables and areas with frequent movement.
- Pros: Highly flexible, resistant to breakage from bending.
- Cons: Slightly higher attenuation compared to solid copper.
3. Copper-Clad Aluminum (CCA)
- Description: Aluminum conductor coated with a thin layer of copper.
- Use: Cost-saving alternative.
- Pros: Cheaper than pure copper.
- Cons: Higher resistance, less reliable, not recommended for high-performance needs.
4. Pure Aluminum
- Description: Occasionally used in budget cables.
- Use: Rarely used due to performance issues.
-Pros: Very low cost.
- Cons: Poor conductivity, higher attenuation, not suitable for most networking needs.
For optimal performance and reliability, solid or stranded copper conductors are recommended.
What AWG is best for Ethernet cable?
For Ethernet cables, the most commonly used American Wire Gauge (AWG) sizes are:
23 AWG
23 AWG typically found in Cat6 and Cat6a cables. Thicker wire, which can support higher frequencies and longer distances. Better performance for Gigabit and 10 Gigabit Ethernet.
24 AWG
It is Common in Cat5E and some Cat6 cables.And suitable for most standard networking needs, including Gigabit Ethernet. More flexible than 23 AWG.
In general, 23 AWG is preferred for higher performance and longer distances, while 24 AWG is sufficient for most typical networking applications.
Why we use 23AWG conductor only?
A 23 AWG Ethernet cable has conductors with a diameter of approximately 0.565mm. While 24 AWG LAN cable's conductors with a diameter of approximately 0.51mm. This 23 awg gauge is typically used in Cat6 and Cat6A cables, which are suitable for high-performance networking applications like Gigabit Ethernet and 10 Gigabit Ethernet.
Inquiry now
